Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids-Test Papers
CBSE Test Paper - 01
Class - 12 Chemistry (Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids)
- Which of the following does not give silver mirror test?
- CH3CH2CHO
- HCOOH
- CH3CHO
- CH3COCH3
- The compound formed as a result of oxidation of ethyl benzene by KMnO4 is
- Benzophenone
- Acetophenone
- Benzoic acid
- Benzyl alcohol
- IUPAC name of CH3CHO is
- Ethanal
- Formaldehyde
- None of these
- Acetaldehyde
- Give the IUPAC name of the following compound:
- 4-bromo-3-methylheptanone
- 3-methyl-4-bromoheptanal
- 4-bromo-3-methylheptanal
- None of these
- The common name for pentanedioic acid is:
- succinic acid
- pimelic acid
- oxalic acid
- glutaric acid
- Write the IUPAC name of the compound:
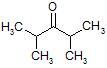
- Give the IUPAC name of the following compound:
(CH3)2C=CHCOOH - Predict the products of the following reaction.
- Write the IUPAC name of the following compound.
(CH3)3CCH2COOH or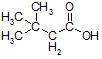
Give chemical reaction to prepare C6H5CH2CH2Br from C6H5CH2CH2COOH
- Describe the following reactions:
- Cannizzaro's reaction.
- Cross Aldol Condensation reaction.
- Write balanced chemical equations for the following reactions.
- Thionyl chloride reacts with benzoic acid.
- Acetic acid is reacted with red phosphorus and HI.
- Acetic acid is treated with Zn metal.
Write the steps for the conversion of ethyl alcohol to acetone.
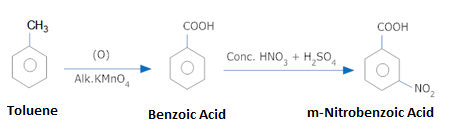
Convert Toluene to m-Nitrobenzoic acid.
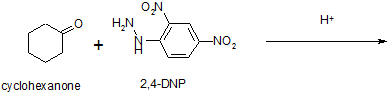
A compound 'A' with formula gives a positive 2, 4 -DNP test but a negative Tollen's test. It can be oxidizing to carboxylic acid 'B' of molecular formula , when treated with alk. under vigorous conditions. The salt of 'B' gives a hydrocarbon 'C' on Kolbes' electrolytic decarboxylation. Identify A, B,C & write chemical equations.
CBSE Test Paper - 01
Class - 12 Chemistry (Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids)
Solutions
- (d) CH3COCH3
Explanation: CH3COCH3 will not give silver mirror test (Tollens Test). Tollens test is given by aldehydes only and HCOOH is the only acid which gives tollen's test. Ketones does not give tollen's test - (c) Benzoic acid
Explanation: Alkylbenzenes having at least one alpha hydrogen when reacts with KMnO4 then, alkyl group oxidises to COOH group.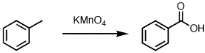
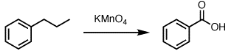
C6H5C2H5 + KMnO4 C6H5COOH - (a) Ethanal
Explanation: CH3CHO is ethanal as we have two carbons in main chain so, the word root is 'Eth' and the functional group is aldehydic group so, suffix is 'al'. Hence, IUPAC name will be Ethanal. - (c) 4-bromo-3-methylheptanal
Explanation:
since functional group CHO is present so it is given first priority and consider a part of main chain. Then name of substituents are given first in alphabetical order followed by word root which is 'hept' and finally suffix which is'al'. - (d) glutaric acid
Explanation: Pentanedioic acid is known as glutaric acid.
(COOH)2 is known as oxalic acid.
Butanedioic acid is known as succinic acid.
hexanedioic acid is known as adipic acid.
heptanedioic acid is known as pimelic acid. 2,4-Dimethylpentan-3-one
3-Methylbut-2-enoic acid
3,3-Dimethylbutanoic acid
C6H5CH2CH2COOH C6H5CH2CH2COO Ag C6H5CH2CH2Br + CO2 + AgBr
- Cannizzaro’s reaction: Aldehydes which do not have an alpha-hydrogen atom, undergo self-oxidation and reduction (disproportionation) reaction on treatment with concentrated alkali.
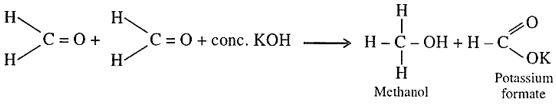
In this reaction, one molecule of the aldehyde is reduced to alcohol while another is oxidised to carboxylic acid salt. - Cross Aldol Condensation reaction: When aldol condensation is carried out between two different aldehydes and/or ketones, it is called cross aldol condensation. If both of them contain alpha-hydrogen atoms, it gives a mixture of 4 products. Following reactions explain cross aldol condensation.
- Cannizzaro’s reaction: Aldehydes which do not have an alpha-hydrogen atom, undergo self-oxidation and reduction (disproportionation) reaction on treatment with concentrated alkali.

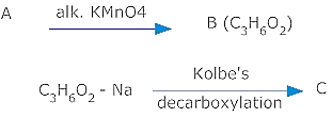
As the compound A gives a positive 2, 4-DNP test but negative Tollen’s test, it is a ketone. Since on oxidation, it gives an acid B, of molecular formula ,it is and B is . As C is obtained by Kolbes decarboxylation of B therefore C is . Therefore A = Pentan -3 one, ; B = Propanoic acid ; and C = Butane . The sequence of reactions are as follows:
CH3 CH2 CO CH2 CH3 CH3CH2COOH + CH3COOH
CH3CH2COOK CH3CH2CH2CH3 + CO2 + KOH + H2