Chemical Kinetics-Test Papers
CBSE Test Paper-01
Class - 12 Chemistry (Chemical Kinetics)
- If 75% of a first order reaction was completed in 32 min, then 50% of the reaction was completed in
- 24 min
- 4 min
- 16 min
- 8 min
- The constant k used in rate equation is known as
- Distance constant
- Velocity constant
- Reaction constant
- Order constant
- The rate constant of the reaction at temperature 200 K is 10 times less than the rate constant at 400 K. The activation energy of the reaction is
- 460.6R
- 921.2 R
- 1842.4R
- 230.3R
- The minimum amount of energy required by the reacting molecules at the time of collisions in order to produce effective collisions is called
- Threshold energy
- Potential energy
- Internal energy
- Activation energy
- Thermal decomposition of a compound is of first order. If 50% of a sample of a compound is decomposed in 120 min, the time taken for 99.9%completion is
- 1000 min
- 399 min
- 1200 min
- 400 min
How does the reaction rate change on increasing the temperature?
Identify the order of reaction from the following rate constant:
What is activation energy?
Time required to decompose SO2Cl2 to half of its initial amount is 60 minutes. If the decomposition is a first order reaction, calculate the rate constant of the reaction.
State any one condition under which a bimolecular reaction may be kinetically first order.
For the chemical decomposition of SO2Cl2, its initial concentration is 0.8420 mol L-1 and final concentration is 0.215 mol L-1 in 2 hours. What is the average rate of this reaction?
- Consider the reaction:
2A + B C + D
Following results were obtained in experiments designed to study the rate of reaction:Exp. No. Initial concentration (mol L-1 ) [A] [B] Initial rate of formation [D] (m/min) 1. 0.10 0.10 2. 0.20 0.20 3. 0.20 0.40 - Write the rate law for the reaction.
- Calculate the value of rate constant for the reaction.
- Which of the following possible reaction mechanism is consistent with the rate law?
Give one example of pseudo first order reaction.
A first order reaction has a rate constant of 0.0051 min-1. If we begin with 0.10 M concentration of the reactant what concentration of the reactant will be left after 3 hours?
Sucrose decomposes in acid solution into glucose and fructose according to the first order rate law with t1/2 = 3.00 hours . What fraction of the sample of sucrose remains after 8 hours.
CBSE Test Paper-01
Class - 12 Chemistry (Chemical Kinetics)
Solutions
- 16 min
Explanation:
75% completion means 2 half lifes so 50% completion means only one half life.
from (1) and (2), we get
t = 16 mins
- 16 min
- Velocity constant
Explanation:
It is describing the speed of a reaction i.e. how concentration of reactant changes w.r.t. time. Hence it is called Velocity constant
- Velocity constant
- 921.2 R
Explanation:
- 921.2 R
- Threshold energy
Explanation:
The minimum amount of energy required by the reacting molecules at the time of collisions in order to produce effective collisions is called threshold energy.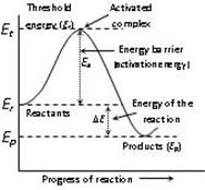
- Threshold energy
- 1200 min
Explanation:
detail:
here,
also,
- 1200 min
The rate of reaction would increase on increasing the temperature as it increases the number of collision as well as number of effective collisions.
Second order, because unit is
Activation energy (Ea) is the minimum amount of energy which the reactant must absorb to cross over the activated complex energy barrier. Mathematically, Ea = ET - ER, where ET is the energy of the activated complex, and ER is the energy of the reactants.
For a first order reaction,
.
.
.If one of the reactant is present in excess, bimolecular reaction will become kinetically first order.
Rate of reaction =
=- Let rate law is
From eq.(ii) and (iii)
2y = 2
y = 1
From eq.(i) and (ii)
2x = 1
x = 0
Thus, the rate is given as Rate =k[B]1 - Rate = k[B]
- B C + E (slow) is the possible reaction with is consistent with the rate law i.e.,
Hence, mechanism II is appropriate for the reaction.
- Let rate law is
rate = k [CH3COOC2H5]1 [H2O]0- Here [R]0 = 0.10 M
t= 3 hours =180 min
k= 0.0051 min-1
Using the formula
= 0.3986
= antilog (0.3986)
= 0.309 M As sucrose decomposes according to the first order rate law,
The aim is to find
= 0.231 hr-1
Hence,
or
or = Antilog (0.8024)
= 6.345
= 0.158