Electrochemistry-Test Papers
CBSE Test Paper-01
Class 12 Chemistry (Electrochemistry)
- Given
- Cu2+ + 2e- Cu, E0 = 0.337 V
- Cu2+ + e- Cu+, E0 = 0.153 V
- 0.52 V
- 0.38 V
- 0.30 V
- 0.90 V
- How much electricity is required in coulomb for the oxidation of 1 mol of FeO to Fe2O3?
- 95000C
- 96000C
- 96487C
- 95550C
- Correct arrangement of Al, Cu, Fe, Mg and Zn in the order in which they displace each other from the solution of their salts is
- Mg > Al > Cu > Fe > Zn
- Mg > Al > Zn > Cu > F
- Mg > Al > Zn > Fe > Cu
- Cu > Al >Zn > Fe > Mg
- In the button cells widely used in watches and other devices the following reaction takes place:
[Given E0 Zn2+/Zn = -0.76V, E0Ag2O/Ag = +0.344V]
Determine Eo cell for the reaction.- 1.104 V
- 1.005 V
- 0.913 V
- 1.159 V
- Conductivity of 0.00241 M acetic acid is 7.896 × 10-5 S cm-1. If for acetic acid is 390.5 S cm2mol-1, what is its dissociation constant?
- 1.75 × 10-5
- 2.05 × 10-5
- 1.95 × 10-5
- 1.85 × 10-5
Write the cell formulation and calculate the standard cell potential of the galvanic cell in which the following reaction takes place:
Fe2+(aq) + Ag+(aq) Fe3+(aq) + Ag(s)
Calculate for the above reaction
[Given:
[1 F = 96500 C mol-1]What is the representation of a Daniell cell?
Why is the voltage of a mercury cell constant during its working?
Suggest a way to determine the value of water?
Molar conductance of 1.5 M solution of an electrolyte is found to be 138.9 S cm2 mol-1 What would be the specific conductance of this solution?
At 298 K, the molar conductivities at infinite dilution of NH4Cl, NaOH and NaCl are 129.8, 217.4 and 108.9s cm2mol-1 respectively. The molar conductivity of 0.01 M NH4OH solution is 9.33s cm2mol-1, calculate the degree of dissociation of NH4OH at this dilution?
Consider the reaction:
What is the quantity of electricity in coulombs needed to reduce 1 mol of ?- The resistance of a conductivity cell containing 0.0001 M KCl solution at 298 K is . What is the cell constant if the conductivity of 0.001 M KCl solution at 298 K is
- Predict the products of electrolysis in the following:
A solution of H2SO4 with platinum electrode.
Zinc rod is dipped in 0.1 M solution of ZnSO4
The salt is 95% dissociated at is dilution at 298 K . Calculate the electrode potential. Given:
E0(Zn2+/Zn) = -0.76Explain construction and working of standard Hydrogen electrode?
CBSE Test Paper-01
Class 12 Chemistry (Electrochemistry)
Solutions
- 0.52 V
Explanation: Eo cell = 2(0.337)-0.153
- 0.52 V
- 96487C
Explanation: For converting FeO to Fe2O3 1mol of electrons are required.
- 96487C
- Mg > Al > Zn > Fe > Cu
Explanation: In application of electrochemical series, the metal which has lower reduction potential has higher tendency to get oxidised and would displace metals with lesser reduction potential from their salt solution.
- Mg > Al > Zn > Fe > Cu
- 1.104 V
Explanation:
E0cell = E0Ag2O/Ag - E0 Zn2+/Zn
= +0.344-(-0.76) = 1.104V
- 1.104 V
- 1.85 × 10-5
Explanation: = 7.896 x 10-5 1000/0.00241 = 32.76Scm2/mol
and = 32.76/390.5 = 0.084
and K = Cα2/1-α = 0.00241 (0.084)2/1-0.084 = 1.85 10-5
- 1.85 × 10-5
= +0.80 V - (+0.77) V
= 0.03 V
= -5790 J mol-1
= 57.90 KJ mol-1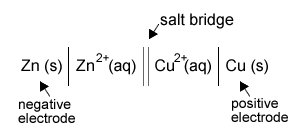
As all the products and reactants are either in solid or liquid state, their concentration does not change with the use of the cell.
Applying Kohlrausch's law of independent migration of ions, the value of water can be determined as follows:
Hence, by knowing the values of HCl, NaOH, and NaCl, the value of water can be determined.- Given that
molarity = 1.5 m
molar conductivity = 138.9 S cm2 mol-1
K = 0.20835 S cm-1
= 129.8 +217.4 - 108.9 = 237.3 5cm2/mol
Degree of dissociation,
= 0.039 or 3.9%.From the given reaction
1 mol of ions requires
= 579000 C of electricity for reduction of Cr3+.- At Anode:
At Cathode:
Overall reaction is:
Using nernst equation for n=2,
= 2.71V - 0.0295V
= 2.6805 V
For free gibbs energy
= -517336.5 J mol-1
= -517.34 KJ mol-1 - At cathode:
At anode:
H2(g) is evolved at cathode and O2(g) is evolved at anode.
- At Anode:
= - 0.7902 VConstruction: SHE consists of a platinum electrode coated with platinum black. The electrode is dipped in an acidic solution and pure Hydrogen gas is bubbled through it. The concentration of both the reduced and oxidized. Forms of Hydrogen is maintained at unity i.e) pressure of H2 gas is 1 bar and concentration of Hydrogen ions in the solution is 1 molar.
Working – The reaction taking place in SHE is At 298 K, the emf of the cell constructed by taking SHE as anode and other half-cell as cathode, gives the reduction potential of the other f cell whereas for a cell constructed by taking SHE as anode gives the oxidation potential of other half cell as conventionally the electrode potential of SHE is zero.