Polymers (Not for Exams)-Test Papers
CBSE Test Paper-01
Class - 12 Chemistry(Polymers)
- Polystyrene is used
- to make rain coats
- as an insulator
- to make handles of utensils
- in paints
- Which of the following statements is not true about low density polythene?
- Inert
- Tough
- Highly branched structure
- Good conductor of electricity
- Painting material among the following is
- Polyvinyl chloride
- Glyptal
- Polystyrene
- Polypropene
- Identify the type of polymer: —A—A—A—A—A—A—
- Copolymer
- Homopolymer
- Condensation polymer
- Biodegradable polymer
- Condensation polymer among the following is:
- Dacron
- Teflon
- Polystyrene
- PVC
Give two examples of synthetic rubber.
Write one use of each - Teflon and polyacrylonitrile.
Classify following as addition and condensation polymer- Bakelite, Polythene, Nylon - 6, 6, Polyacrylonitrile ,Dacron.
- Write the monomers used for getting the following polymers:
- Polyvinyl chloride
- Teflon
- Bakelite
- During war, accidents or street quarrels, sometime people get deep injuries which require stitching of wounds. Earlier these wounds used to be stitched by nylon thread which was non-biodegradable. This thread used to be pulled out after healing of wounds. This process caused pain to the patients. But these days biodegradable polymer is used for stitching of wounds which gets degraded by itself within a week or so.
Now, answer the following questions:- Write the name of the biodegradable polymer used for stitching of wounds after operation.
- What are the monomer units of this polymer.
Is
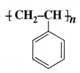 a homopolymer or a copolymer?
a homopolymer or a copolymer? What are thermoplastic and thermosetting polymers? Give one example of each.
Explain the terms polymer and monomer.
What are the monomeric repeating units of Nylon- 6 and Nylon- 6, 6?
How are polymers classified on the basis of structure?
CBSE Test Paper-01
Class - 12 Chemistry(Polymers)
Solutions
- (b) as an insulator
Explanation: Polystyrene is a thermoplastic polymers which are the linear or slightly branched long chain molecules capable of repeatedly softening on heating and hardening on cooling. It is used as an insulator. - (d) Good conductor of electricity
Explanation: Low density polythene is chemically inert and tough but flexible and a poor conductor of electricity. It has highly branched structure. Hence, it is used in the insulation of electricity carrying wires. - (b) Glyptal
Explanation: Gyptal is a polyester formed from condensation of ethylene glycol and phthalic acid. It is used in paints and lacquers. - (b) Homopolymer
Explanation: Since only one monomeric unit is present. So, it is a homopolymer. - (a) Dacron
Explanation: The formation of terylene or dacron by the interaction of ethylene glycol and terephthalic acid is an example of this type of condensation polymerisation - Example of synthetic rubber - Neoprene, Buna – N etc.
- Uses:
- Teflon is used in making oil seals, gaskets & for non-stick surface coating of utensils to make them non-sticky
- Polyacrylonitrile is used for wool in making commercial fibres as orlon or acrilan which is used for making carpet and blankets
Addition polymer Condensation polymers Polythene Dacron Polyacrylonitrite Nylon - 6, 6, and Bakelite - Vinyl chloride
- Tetrafluoroethylene
- Formaldehyde () and phenol
- Nylon-2-Nylon-6
- monomer of Nylon 2 Nylon 6 is Glycine and Amino caproic acid
Homopolymer and monomer is Styrene
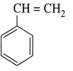
- Thermoplastics Polymers: Thermoplastics are linear polymers which can be repeatedly softened on heating and hardened on cooling and hence can be used again and again without any change in chemical composition and mechanical strength. Example - Polythene.
- Thermosetting Polymers: Thermosetting polymers are permanently setting polymers. On heating in a mould, they get hardened and set and cannot be softened again. This hardening on heating is due to cross-linking between different polymer chains to give a three-dimensional network solid. Example - Bakelite.
- Polymer. Polymers are defined as high molecular mass macromolecules which consists of repeating structural units derived from the corresponding monomers.
- Monomers. Simple and reactive molecules from which the polymers are prepared either by addition or condensation are called monomers. For example, ethane, vinyl chloride, acrylonitrile etc.
The monomeric repeating unit of Nylon 6 is , which is derived from Caprolactam.
The monomeric repeating unit of Nylon 6, 6 is , which is derived from hexamethylene diamine and adipic acid.- Polymers are classified on the basis of structure as follows:
- Linear polymers:
These polymers are formed of long straight chains. They can be depicted as:
For e.g., high density polythene (HDP), polyvinyl chloride, etc.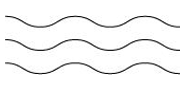
- Branched chain polymers:
These polymers are basically linear chain polymers with some branches. These polymers are represented as:
For e.g., low density polythene (LDP), amylopectin, etc.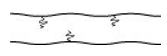
- Cross-linked or Network polymers:
These polymers have many cross-linking bonds that give rise to a network-like structure. These polymers contain bi-functional and tri-functional monomers and strong covalent bonds between various linear polymer chains. Examples of such polymers include bakelite and melmac.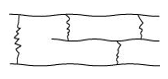
- Linear polymers: