Coordination Compounds-Test Papers
CBSE Test Paper-01
Class - 12 Chemistry (Coordination Compounds)
- Tetraaminecopper(II) ion is a square planar complex with one unpaired electron. According to valence bond theory the hybrid state of copper should be
- dsp2
- sp3d2
- d2sp3
- sp3
- Which of the following pair contains a complex salt and double salt respectively?
- [Cu(NH3)4]SO4, FeSO4.7H2O
- FeSO4, K4[Fe(CN)6]
- MgSO4.7H2O, CuSO4
- [Cu(NH3)4]SO4, K2SO4.Al2(SO4)3.24H2O
- The type of isomerism that is exhibited by [Co(NH3)5SO4]Br and [Co(NH3)5Br]SO4 is:
- Linkage isomerism
- Solvate isomerism
- Ionisation isomerism
- Coordination isomerism
- The oxidation number of Fe in K4[Fe(CN)6] is
- 0
- +1
- +3
- +2
- The anti pernicious anaemia factor which is a coordination compound of Cobalt is:
- Cyanocobalamine
- Haemoglobin
- Desferrioxime B
- Carbonic anhydrase
Write formula for Hexammineplatinum (VI) Chloride.
What is the coordination number of central metal ion in [Fe(C2O4)3]2-.
Write formula forTetramminedichloridooplatinum (IV) Bromide.
What are the different shapes or coordination polyhedra in the complexes?
Name a ligand which is bidentate and give an example of the complex formed by this ligand.
Give the chemical formula of pentaammine chloro cobalt (III) chloride.
[NiCl4]2- is paramagnetic while [Ni(CO)4]is diamagnetic though both are tetrahedral. Why?
- Draw the structures of following:
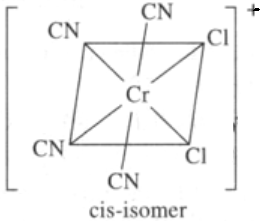
- cis-dichlorotetracyanochromate(III)
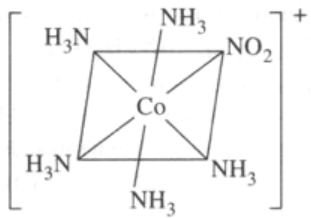
- Pentaamminenitrito-N-cobalt(III)
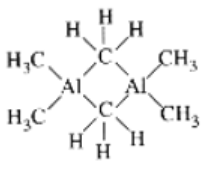
- Hexamethyldialuminium
Which isomerism is shown by a compound having ambidentate ligand? Give example.
Explain with two examples each of the following: Coordination entity, ligand coordination number, coordination polyhedron, homoleptic and heteroleptic.
CBSE Test Paper-01
Class - 12 Chemistry (Coordination Compounds)
Solutions
- (a) dsp2
Explanation: Tetraaminecopper(II) ion is square planar. Square planar complexes have dsp2 hybridisation. So hybridization is dsp2. - (d) [Cu(NH3)4]SO4, K2SO4.Al2(SO4)3.24H2O
Explanation: [Cu(NH3)4]SO4 this is a complex salt because it contains a coordination entity (central metal ion Cu2+ with 4 ligand molecules of NH3 in coordination sphere) while K2SO4.Al2(SO4)3.24H2O is double salt as it can dissociate completely into simple ions when it is dissolved in water. - (c) Ionisation isomerism
Explanation: Ionisation isomerism arises when the counter ion in a complex salt is itself a potential ligand and can displace a ligand which can then become a counter ion. Here Br- and SO42- exchanged places as counter ion and ligand. So these complexes exhibit ionisation isomerism. - (d) +2
Explanation: The ligand CN- has charge of –1. So the overall charge carried by 6 CN- ligands is -6. Each potassium ion K+ carries a charge of +1. So 4 potassium ions carry an overall charge of +4. This implies that the overall charge on the coordination sphere is -4 to balance the +4 charge of the potassium ions. Let the oxidation number of Fe be x. Then
x + (-6) = -4
x = -4 - (-6)
x = -4 + 6
x = +2
So, the oxidation number of Fe is +2. - (a) Cyanocobalamine
Explanation: Vitamin B12, cyanocobalamine, the antipernicious anaemia factor is a coordination compound of Cobalt. [Pt (NH3)6]Cl6
Six
[Pt Cl2(NH3)4]Br2
- The various coordination polyhedra are –
- Octahedral

- Tetrahedral
- Square Planar
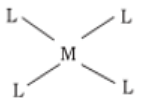
- Trigonal bipyramidal
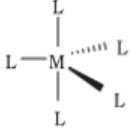
- Square pyramidal
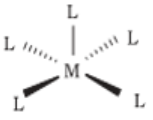
- Octahedral
Ethylene diamine (en) is bidentate ligand [Co(en)3]3+. Its IUPAC name is tris (ethylene diamine) cobalt (III) ion.
[CO(NH3)5Cl]Cl2
In [NiCl4]2-Ni is in +2 oxidation state electronic configuration = 3d84s0 .

Cl- is a weak ligand. It cannot pair up the electrons in 3d orbitals. Hence, it is paramagnetic. In [Ni(CO)4], Ni is in zero oxidation state and configuration
is -3d84s2.
In the presence of CO ligand, the 4S electrons shift to 3d to pair up 3d electrons. Thus, there is no unpaired electron present. Hence it is diamagnetic.- Structures of the three complex ions/molecules are given below:
A complex having ambident ligand will show linkage isomerism e.g [Cr(NH3)5(NO2)]Cl2 has NO2- as ambident Ligand and its Linkage isomer will be [Cr(NH3)5(ONO)]Cl2.
Coordination entity: This entity usually constitutes a central metal atom or ion, to which are attached a fixed number of other atoms or ions or groups by coordinate bonds. Examples are [Ni(CO)4], [COCl3(NH3)3], etc.
Ligands: It is an ion having at least one lone pair of electrons and capable of forming a coordinate bond with central atom / ion in the coordination entity.
Examples are : Cl-, (OH)-, (CN)-etc.
Coordinate number: The total number of coordinate bonds with which central atom/ ion is linked to ligands in the coordination entity is called coordination number of central atom / ion.
Coordination polyhedron : The spatial arrangement of the ligands which are directly attached to the central atom / ion defines a coordination polyhedron about the central atom.
Examples are: [Co(NH3)6]3+is octahedral,
[Ni(CO)4]is tetrahedral.
Homoleptic and hedroleptic: Complexes in which a metal is bound to only one kind of donor groups are known as homoleptic.
Example [CO(NH3)6]3+
Complex in which a metal is bound to more than one kind of donor groups are called hetroleptic. Example : [Co(NH3)4Cl2]+